Image range of interest
Range of interest when applied to an image changes its visual appearance: pixels outside the range lose their colors to black and white. This gives you an additional possibility to visually emphasize some area on the image.
Some IRT Analyzer features use image range of interest for their needs. For example, hot/cold spot are detected only within pixels in this range.
To set range of interest, right click on the image and select 'Range of Interest' in the context menu.
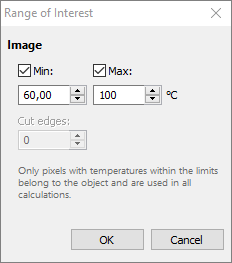
Range of interest can have only the bottom limit, only the top limit or both limits enabled:
1.When only the bottom limit (Min) is enabled, active pixels are the pixels with temperatures above the bottom limit.
2.When only the top limit (Max) is enabled, active pixels are the pixels with temperatures below the top limit.
3.When both limits are enabled, pixels with temperatures inside the min-to-max range are active.
Range of interest for area objects
Range of interest, if set for an area, defines pixels which belong to that area. For example, you have created a rectangle. If you assign some temperature range to it, IRT Analyzer will take into account only those pixels of the rectangle that fall into the defined range – the rest will not belong to the object.
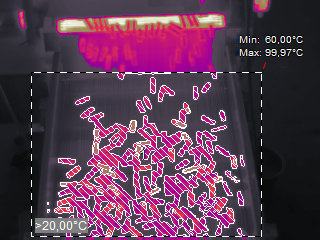
Only the crosshatched pixels at the picture belong to the area object and only they are taken when the histogram of object area is calculated. It is also true for other operations with areas – min, max, average calculation, trend analysis, region where the filters are applied and so on.
Range of interest for areas is defined using image temperatures, which can be different to the object temperatures (in case of different emissivity, for example). This is done to prevent object shape changing when you change its emissivity. |
Range of interest for area objects have an additional parameter - 'Cut Edges'. Edges are image points at which temperature changes sharply. When 'Cut Edges' is bigger than 0, IRT Analyzer finds edges inside the area and removes them from the resulting region. The bigger this parameter is the bigger the tolerance for the edge detection algorithm (more edges detected). Cut Edges function can be useful, as edges (because of spatial resolution of the camera detector) often do not show real temperature values and it is better not to use them in calculations.
Object area (pixel count) calculation Range of interest defined for an area and for the image affects object area calculation. Pixels that do not belong to the range of interest (both image and area) are not counted. |


