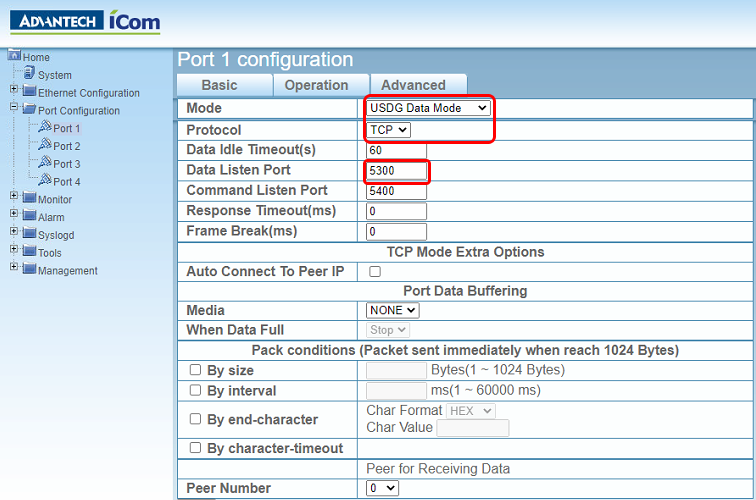
Device type
Supported devices include Endurance, MI3 and Thermalert 4.
IRT KilnMonitor does not support configuration of all parameters a pyrometer may support, it only polls already configured devices. Some extra parameters can be set using Special commands, but communication related parameters like baud rate, multidrop address or IP address must be configured in the special software delivered with pyrometers.
Connection
Depending on your device type connection can be TCP/IP or Serial. Serial is used when RS485 device is connected to a COM port. TCP/IP is used if the pyrometer has Ethernet interface or if you connect RS485 pyrometer with RS485 to Ethernet converter without virtual COM ports (see RS485 to Ethernet converter below).
Baud rate: you should select the baud rate that matches the baud rate the pyrometer is currently configured for. If baud rates do not match, communication is not possible, baud rate auto negotiation is not supported.
Unit: RS485 multidrop unit address.
Head: head address for devices that support several sensing heads (MI3).
Poll frequency: IRT KilnMonitor will try to poll the pyrometer for measured temperatures at this rate. The selected rate might not be achieved when response time of the device is slower or when there are several devices connected to the same RS485 multidrop network. Also sometimes it makes no sense to poll too frequently as pyrometer may not update its reading fast enough. Please consult the pyrometer manual for response times and update frequencies.
Parameters
Emissivity: the kiln shell usually have surface with high emittance, so emissivity value should be around 0.95.
Transmissivity: this parameter is used to compensate thermal radiation losses because of atmospheric absorption. Pyrometers are usually installed close to the kiln, so transmissivity is normally close to 1.0.
Maximum internal temperature: if the specified temperature value is exceeded, a system state alarm is generated.
Special commands
List of additional pyrometers commands that will be executed immediately after connection to the pyrometer is established. Please refer to the pyrometer manual for a list of possible commands.
Each command should be on its own line. To have more than one command on a line, commands must be separated with a semi-colon.
Commands should be entered without unit/head addresses! Temperature unit in commands is Celsius.
RS485 to Ethernet converter
The usual way of connecting an RS485 device to a PC is to use special RS485 boards or RS485 to RS232 converters and talk to the device through a corresponding COM port. There is also another possibility - to use an RS485 to Ethernet converter. Such converters work in a way that they convert RS485 data into TCP/IP packets and back. On the PC side they create virtual COM ports and send data through them as if the remote device is directly connected to the PC COM port. This fully simulates serial communication and PC software does not even know that Ethernet is used in the middle.
Converter to Ethernet can also work without creating virtual COM ports on the PC side. Then they just convert RS485 data to TCP/IP packets and PC software should establish connection using TCP sockets. IRT KilnMonitor supports this method as well - use the Ethernet connection option.
Advantech EKI-1524
Here is a only a brief description for the two modes for Advantech EKI-1524 converter. For details please check the CS400 hardware manual.
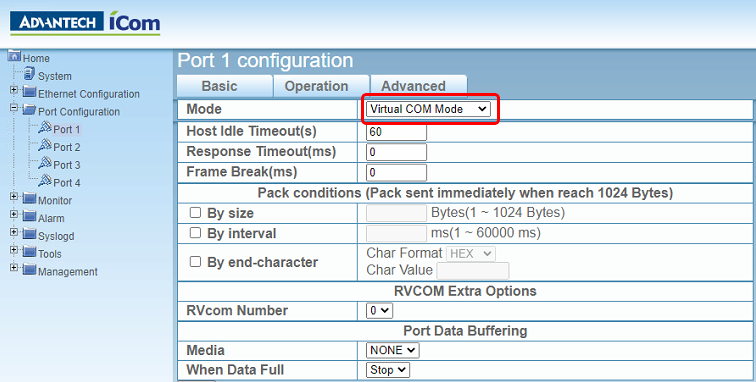
In the port configuration if you select Virtual COM Mode, you will need to install Advantech software on the PC and use virtual COM ports there.
You can also use USDG Data Mode with TCP protocol. Then Advantech software and virtual COM ports are not needed on the PC side. In IRT KilnMonitor you select Ethernet connection option. IP address is the address of the EKI-1524 device and Port is the port number selected in the EKI-1524 Port configuration: